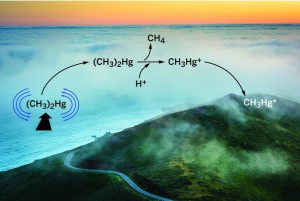
This figure is from a recent article written about the research in Chemical and Engineering News. Ocean eddies bring (CH3)2Hg from deep water to the surface, where the (CH3)2Hg evaporates. Acidic fog or aerosol particles in the atmosphere demethylate (CH3)2Hg to form CH3Hg+, which is then deposited on coastal land.
Fog Water Harvesting Solutions for Coastal California
The Peter Weiss-Penzias Lab at UC Santa Cruz * image below by Anja Ulfeldt*